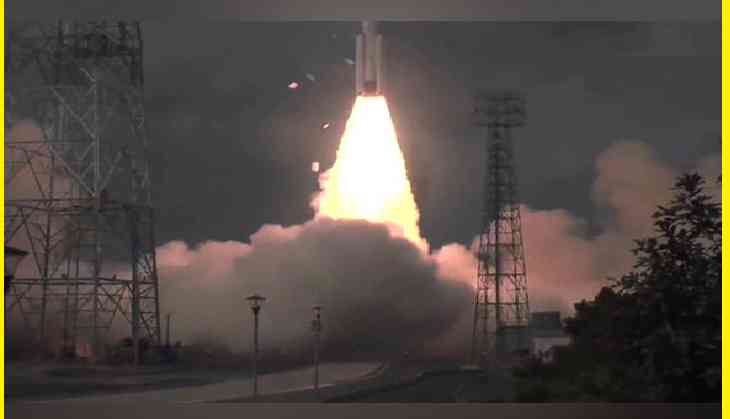
The PSLV-C54 rocket of the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), carrying nine nano satellites, successfully lifted off from Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Andhra Pradesh's Sriharikota on November 26.
The rocket that carries EOS-06, also known as Earth Observation Satellite – 06 among other passenger satellites, was launched from the First Launch Pad (FLP) Sriharikota spaceport at 11.56 am in a two-hour multi-orbit launch mission.
Notably, it was the 56th flight of the Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV), one of the most trusted rockets of the ISRO. This was also the final mission for the year (2022) for the PSLV-C54 rocket.
The PSLV-C54 rocket’s final pay load was the EOS-06. In Orbit 1, it was separated successfully.
“EOS-06 spacecraft separation is successful. The spacecraft's health is normal. The mission is continuing,” ISRO tweeted.
"Subsequently, Orbit change is planned by using two Orbit ChangeThrusters (OCTs) introduced in the Propulsion Bay Ring of the PSLV-C54 Vehicle. The Passenger Payloads (PPLs) will be separated in Orbit-2," read a statement by ISRO.
The eight nano-satellites that are a part of the mission include the diplomatic satellite Nano Satellite-2 for Bhutan (INS-2B), a hyperspectral satellite Anand for Bengaluru-based tech start-up Pixxel, Thybolt-1 and Thybolt-2 from Dhruva Space, and four satellites for US-based Spaceflight.
The mission objective is said to be to ensure the data continuity of Ocean colour and wind vector data to sustain operational applications.