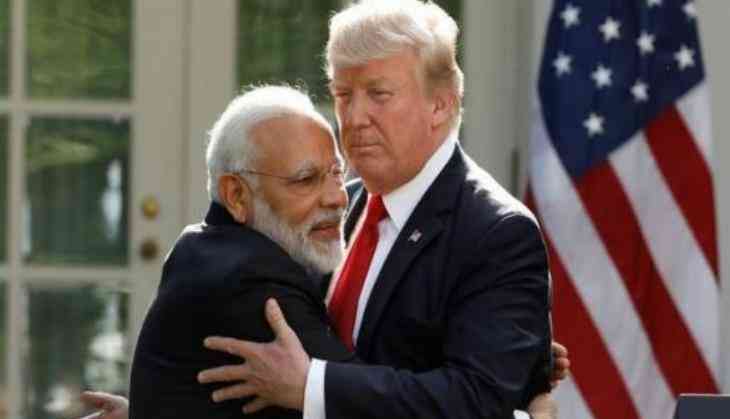
The U.S. Department of Defense and Department of State have submitted a joint report to the Congress, in which it has reiterated the support by the United States towards the inclusion of India in the elite Nuclear Suppliers Group (NSG).
The United States has also re-affirmed its support for India's membership in the Australia Group and Wassenaar Arrangement as soon as India meets each group's membership criteria.
Since 2010, the United States has supported India's membership in the four multilateral export control regimes-Wassenaar Arrangement, NSG, Australia Group, and the Missile Technology Control Regime.
The report was on enhancing defense and security cooperation with India in accordance with section 1292 of the National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA) for Fiscal Year 2017.
The report includes joint actions taken by the Secretary of Defense and Secretary of State necessary to:
(A) Recognize India's status as a Major Defense Partner of the United States;
(B) Designate an individual within the executive branch who has experience in defense acquisition and technology to reinforce, through interagency coordination, the success of the Framework for the U.S.-India Defense relationship and help resolve remaining issues impeding defense trade, security cooperation, and co-production and co-development opportunities;
(C) Approve and facilitate the transfer of advanced technology, consistent with U.S. conventional arms transfer policy, to support combined military planning with India's military for missions such as humanitarian assistance and disaster relief, counter-piracy, freedom of navigation, and maritime domain awareness missions, and to promote weapons systems interoperability;
(D) Strengthen the effectiveness of the U.S.-India Defense Technology and Trade Initiative and the durability of the Department of Defense's "India Rapid Reaction Cell";
(E) To collaborate with the Government of India to develop mutually agreeable mechanisms to verify the security of defence articles, defence services, and related technology, such as appropriate cyber security and end-use monitoring arrangements, consistent with U.S. export control laws and policy;
(F) Promote policies that will encourage the efficient review and authorization of defence sales and exports to India;
(G) Encourage greater government-to-government and commercial military transactions between the United States and India;
(H) Support the development and alignment of India's export control and procurement regimes with those of the United States and multilateral control regimes; and (I) continue to enhance defence and security cooperation with India in order to advance the United States interests in South Asia and the greater Indo-Asia-Pacific region.
The National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA) 2017 also directs the Department to reorganize the Office of the USD (AT&L) into two new Under Secretary positions-one for Research and Engineering (USD (R&E)) and one for Acquisition and Sustainment (USD (A&S)). This change will take effect not later than February 2018.
"With a mutual aim for global stability, the United States and India maintain a broad-based strategic partnership and have an increasing convergence of interests, including on maritime domain awareness, counter-piracy, counter-terrorism and coordinated response to transnational threats." the joint report said.
It further stated, " We see a growing convergence with India on our strategic outlook for the region, and we view India as an increasingly important regional security partner within and beyond the Indo-Asia-Pacific region."
Adding, "India has deepened its involvement with the biennial Rim-of-the-Pacific (RIMPAC) exercise hosted by U.S. Pacific Command. In 2017, the United States expects to relaunch our bilateral Air Force exercise, COPE INDIA. The U.S. Air Force is also focused on expanding cooperation with the Indian Air Force on C-130J/C-17 transport aircraft capabilities, flight safety, humanitarian assistance and disaster relief, and combat search and rescue."
The U.S. DoD and the Indian MOD have a robust International Military Education and Training (IMET) program that brings Indian military personnel to U.S. institutions for training.
For India, seven of the last nine Indian Navy Chiefs have been U.S. professional military education graduates. For Fiscal Year 2017, the Department of State allocated $1.3 million in International Military Education and Training funds for India.
The United States designated India a "Major Defense Partner" in June 2016 - a status unique to India. The designation is intended to elevate defence trade and technology sharing with India to a level commensurate with that of U.S. closest allies and partners. It also seeks to institutionalize changes the United States has made to ensure strong defence trade and technology cooperation.
The momentum behind the relationship and converging security interests will result in a more secure Indo-Asia Pacific region and beyond.After Prime Minister Modi's June 2016 visit, the United States and India released the "Framework for the U.S.-India Cyber Relationship," which recognizes the value of enhancing and institutionalizing our broad-based cooperation on cyber issues.
The framework highlights priority areas for U.S.-India cyber cooperation including strengthening critical internet infrastructure and undertaking skill development and capacity building programs.
-ANI