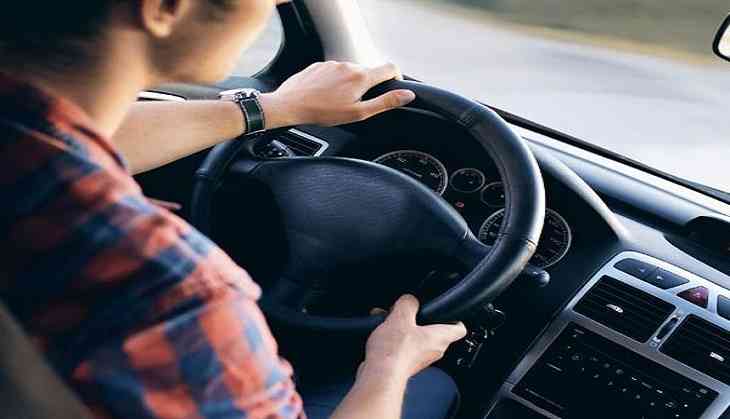
Word of caution! Use of marijuana, in combination with alcohol by drivers, is especially dangerous, according to a latest study.
Drivers, who use both of them, are five times more likely to be responsible for causing fatal two-vehicle crashes than sober drivers involved in the same crashes.
According to researchers from Columbia University, when the two were used in isolation, alcohol and marijuana increase crash culpability by 437 percent and 62 percent, respectively.
"The risk of crash initiation from concurrent use of alcohol and marijuana among drivers increases by more than fivefold when compared with drivers who used neither of the substances," said Guohua Li.
They analyzed data for 1,4,742 drivers involved in fatal two-vehicle crashes between 1993 and 2014.
Crashes involving single vehicles, more than two vehicles, commercial trucks, and two- vehicle crashes in which both drivers were responsible were excluded from the analysis.
Drivers who were responsible for the crashes were significantly more likely than non-culpable drivers to test positive for alcohol (28 percent vs. 10 percent), marijuana (10 percent vs. 6 percent), and both alcohol and marijuana (4 percent vs. 1 percent).
Drivers who tested positive for alcohol, marijuana, or both were more likely than those who tested negative to be male aged 25 to 44 years and to have had a positive crash.
The three most common driving errors that led to these fatal crashes were failure to keep in proper lane (43 percent), failure to yield right of way (22 percent), and speeding (21 percent).
"While alcohol-impaired driving remains a leading cause of traffic fatalities in the United States, driving under the influence of marijuana and other drugs has become more prevalent in the past two decades," Dr. Li concluded.
The findings are published in the journal Annals of Epidemiology.
-ANI