Uttarakhand: Lightning strikes kill 26 goats, learn how to protect yourself during thunderstorms
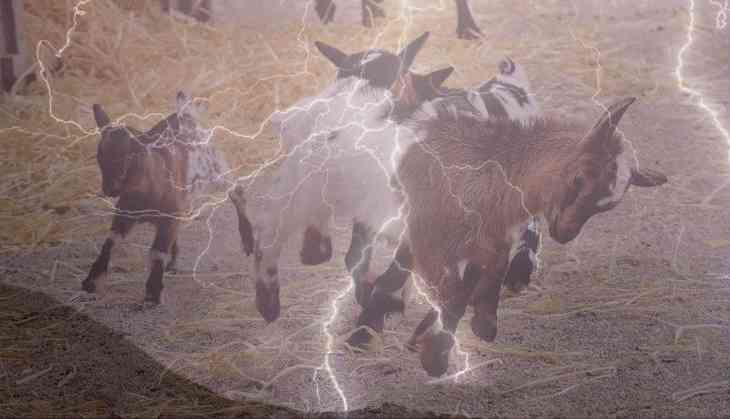

In a tragic incident, lightning strikes claimed the lives of 26 goats in the Uttarkashi district of Uttarakhand. The incident occurred on Wednesday while the goats were grazing near Kamar village Tok in the Bhatwadi block of Uttarkashi.
Discovery of the Tragedy
The Disaster Operation Center officials were alerted about the incident and immediately responded to the scene. Upon inspection, it was determined that out of the 26 deceased goats, 19 belonged to shepherd Mahendra Singh, 2 belonged to Hukm Singh, and 5 belonged to Narayan Singh.
Investigation and Response
The Animal Husbandry Department, in collaboration with the revenue team, promptly arrived at the location upon receiving news of the goats' demise. Their purpose was to assess the situation and gather information to prevent further losses.
Lightning Impact on Humans and Animals
Lightning is a powerful discharge of electricity that occurs during thunderstorms. It poses a significant threat to both humans and animals, with potentially fatal consequences. When lightning strikes, it can cause severe injuries or even death due to the following reasons:
- Direct Strikes: In some cases, lightning can strike an individual or an animal directly. This occurs when the electrical discharge makes contact with the body, resulting in severe burns, organ damage, cardiac arrest, or neurological trauma. The intense heat generated by a lightning bolt can also ignite clothing or fur, leading to secondary injuries.
- Ground Currents: Lightning strikes often induce ground currents that can travel through the earth's surface. If a human or animal is in close proximity to the point of impact, these ground currents can pass through their bodies, causing electric shock injuries. The severity of the shock depends on factors such as the current's strength and the duration of exposure.
- Side Flashes: Side flashes occur when lightning strikes an object, such as a tree or a building, and then jumps to a nearby individual or animal. This phenomenon can happen if the person or animal is in close proximity to the object struck by lightning. Side flashes can cause injuries similar to those resulting from direct strikes.
- Step Voltage: Step voltage refers to the potential difference that occurs between two points on the ground due to the flow of lightning-induced ground currents. When lightning strikes the ground, the electric current disperses in a radial pattern. If a person or animal is standing or lying on the ground within this area, they can experience a voltage difference between their feet, resulting in electric shock injuries.
Tips for Thunderstorm Safety
- Seek Shelter: When thunderstorms are approaching, find a safe location indoors. A sturdy building or a fully enclosed vehicle with a metal roof offers the best protection. Avoid open spaces, tall trees, bodies of water, and metal objects during a thunderstorm.
- Stay Informed: Pay attention to weather forecasts and thunderstorm warnings issued by local authorities. Stay updated on the progress of the storm to make informed decisions regarding your safety.
- Avoid Electronic Devices: During a thunderstorm, it's advisable to stay away from electronic devices such as computers, televisions, and corded phones. Unplug them to minimize the risk of electric shock in case of a lightning strike.
- Stay Away from Windows and Plumbing: Avoid direct contact with windows, plumbing fixtures, and electrical equipment. Lightning can travel through these systems, potentially causing harm.
- Wait it Out: If you are caught outside during a thunderstorm, do not seek shelter under trees or other tall objects. Instead, find a low-lying area and crouch down with your feet together, minimizing your contact with the ground.